Origins of the Great Fair Rockville Maryland (1846-1932)
In 1846, James K. Polk was President of the United States, the U.S. flag had only 28 stars on it, and less than 1,500 people lived in Rockville. It also was the year that the Montgomery County Agricultural Society was organized, that began the tradition of the Montgomery County Fair in Rockville. A 12-member board of directors was chosen, headed by John P. C. Peter, President. The Montgomery County Fair opened two years later on the Pike in 1848, about where Richard Montgomery High School is today.
Discussions about farm improvements led to organized agricultural efforts. In 1846, Rockville farmers helped to establish the Montgomery County Agricultural Society. Two years later, Court House Square overflowed with displays of agricultural implements at the first county fair. The register of will opened his office for exhibits of household manufacturers. and the county clerk’s place teemed with fruits and vegetables. Women competed for cash prizes in the categories of homespun fabrics, fancy handwork, pickles, preserves, butter, cheese, and honey. Men exhibited livestock on the grounds of the Beall-Dawson House.
In a few years, the fair moved to Samuel T. Stonestreet’s woodlot adjacent to Saint Mary’s Church. The annual fair became a week-long gathering to showcase innovation, compete, and socialize. The property on the Rockville Pike was used until 1932, after which much of the land became Richard Montgomery High School.
From The Baltimore Sun Newspaper on September 20, 1848:
The Montgomery County Agricultural Fair held at Rockville, Maryland on Thursday and Friday last, the Journal of that place says, fully met the most sanguine expectation of its friends. The concourse of people was very large, and the stock, implements, and other articles exhibited, were the most perfect and beautiful. The Journal designs to publish the various reports of the committee—and the very able and interesting address of R. J. Bowie, Esq., and the other appropriate remarks submitted on the occasion, and says:
The exhibition was highly credible to the officers and members of the club, and to our country. We must reserve, for a more lengthy notice, the beautiful stock and implements of agriculture sent by gentlemen residing out of our county. We are gratified, indeed, that every thing went off gloriously, and the occasion will be long remembered by all who were present.
All the latest improved machinery in farm and garden implements were there, together with wagons, carriages, automobiles, trucks, and tractors. The display of cattle, sheep and hogs had long been one of the leading features at the Rockville Fair. Many fine herds of cattle, including Jerseys, Guernseys and other varieties were on exhibition. Two hundred of the finest horses in Montgomery County, along with many from the District of Columbia, nearby Virginia, and elsewhere were on exhibition.

Fair-goers in their finest stroll along the midway. Hats were a fashion requirement at the time, as were long flowing dresses and suits. Photo by Lewis Reed, ca. 1910
Many other attractions were provided, including the midway, merry-go-round, Ferris wheel, side shows, free exhibitions in front of the grandstand, horse racing, pony races, mule races, automobile contests, a parade of stock, horse show, dog show, poultry show, an automobile show, and clay pigeon shoots. The clay-pigeon shoot was one of the biggest events of its kind ever held in Maryland.
The various departments were filled to overflowing with high-class exhibits. The main exhibition hall was devoted to farm products and garden products, household displays, flowers, fruits, etc. The household department had an endless array of preserves, jellies, canned fruits, bread, cakes, candles, pies, fancy articles, and works of art. Sanders & Stayman and E. F. Droop & Co. of Washington, had excellent displays of musical instruments in this hall. Examples of locally grown produce were abundant in the main hall. Peaches, apples, plums, damsons, cantaloupes and watermelons were piled up in tempting array. The poultry show was also a place of interest. Many fine chickens, turkeys, geese, ducks and pigeons were being shown.
The Fair was always attended by large numbers of out-of-town visitors from other Maryland counties like Frederick, Howard, and Carroll counties, as well as attracting out-of-state fair-goers from the District of Columbia and neighboring counties in Virginia. Vehicles were assigned places all around the fairgrounds, and the park was completely surrounded. What is fascinating to me is, with all of these early cars painted in black, how on earth would you find your car?

Montgomery County Fairgrounds Poultry House boarded up for the winter. Photo by Lewis Reed, ca. 1910

Sign on the left side of the building reads, “The Beautiful Caverns of Luray Souvenirs”. Photo by Lewis Reed, ca. 1910
The Race Track
If only the grandstands at the Rockville Fairgrounds could talk. The stories it could tell – it would tell stories of great racing – first on horses, bicycles and motorcycles, and then in cars. This grandstand could talk about the rich history of racing that took place on the one-third of a mile long dirt track which attracted high-power cars operated by some of the most noted speed kings of the country.
When Lewis Reed took these photographs in the early 1900s, the Rockville fairgrounds had undergone a significant upgrade. The grounds were enlarged by the addition of about five acres, allowing for the construction of a one-third of a mile race course along with a new grandstand, and improvements were made to the buildings and grounds, bringing them up-to-date in every respect. Montgomery County could well boast one of the nicest fairgrounds in the state.
Below is a previously unpublished Program of Speed Contests held in Rockville, Maryland, dated September 4 and 5, 1890. The program is from Lewis Reed’s collection. (click on photos for larger images)

Front cover of a racing program from the 1890 Montgomery County Agricultural Society Fair. From Lewis Reed’s Collection.

Racing program from the 1890 Montgomery County Agricultural Society Fair. From Lewis Reed’s Collection.

Back cover of racing program from the 1890 Montgomery County Agricultural Society Fair. From Lewis Reed’s Collection.
Bicycle Races
Bicycle races became very popular throughout the country and were a novel event at the Rockville Fairgrounds as early as 1915. The track was a one-third of a mile dirt racing oval with wide, sweeping curves and a grandstand for spectators, which made for clear views. Notice the riders are in shirts and ties. In the background: according to the 1903 Sanborn Fire Insurance Atlas of the fairgrounds, these structures near the track were used as cattle pens.

This circa 1915 photo of an early bicycle race at the Rockville Fairgrounds gives a sense of just how popular the sport was at the time. Photo by Lewis Reed
Harness Races
Harness racing was one of the main attractions at the new race track before the introduction of the automobile and the subsequent popularity of racing cars. Horses were harnessed to lightweight one-seater buggies called sulkies, and would race around the track at a trot, as opposed to the galloping gait of horses ridden by jockeys.

Harness race at the Rockville Fair, circa 1910. All those throngs of people had plenty to see. Photo by Lewis Reed

Harness racers rounding the bend on the racetrack, Rockville Fairground circa 1910. Photo by Lewis Reed

Race horses and two-wheeled sulkies (for trotting races) at the Rockville Fairground stables, Photo by Lewis Reed, ca. 1910.

Race horse and two-wheeled sulkies (for trotting races) at the Rockville Fairground stables. Photo by Lewis Reed ca. 1910
First Auto Races at Rockville Fair Speedway
From The Baltimore Sun, August 27, 1923:
This is the first year that a Rockville Fair has continued through Saturday. The extra day was added this time as an experiment, the management believing that by substituting new features the additional day could be made a success. Automobile races, the first ever held at Rockville, were the day’s principal attraction and they attracted a good-sized crowd.
Early action shots like the ones below are rare, however, Lewis Reed was there to capture six epic moments of race history through the lens of his camera that day.

Dusty Action – 1923 photo of the exciting auto races at Rockville Fair. Five racers are just coming around the bend on this dirt track with their tires spinning up dust in their wake. Photo by Lewis Reed

Race car drivers deep in dust round a turn at the Rockville Fair auto races. Print made from a Lewis Reed glass negative.

High-powered race cars rounding a wide, sweeping curve at the Rockville Fair auto races, August 25, 1923. Print made from a Lewis Reed glass negative

Two-man race car. Some early race cars included both a driver and a ‘riding mechanic’. One of the key jobs of the second man in a race car was to look backward and alert the driver to what was going on behind him. Photo by Lewis Reed
Early race car drivers were required to have a riding mechanic, otherwise it was voluntary. Riding mechanics, who in addition to being lookouts, kept an eye on tire wear and would even hop out of the car and run back through the infield to get fuel. Special note: The above photograph was featured as a part of the London Array Series of “Impossible Engineering,” broadcast on January 24, 2019 on Discovery’s Science Channel. The photograph was used on the program that featured a segment on the development of the race car.
Rockville Garage Displaying New Model Cars at the Rockville Fair Grounds, 1918

Anybody for a demonstration drive? Identified by the triangle logo on the grill and the number of passengers seated in it, the car appears to be a 1918 Hudson Super Six Seven Passenger Touring. Photo by Lewis Reed
Reed Brothers Company Softball Team at the Rockville Fairgrounds, late 1920s
From a distance, it looks and sounds like a regular baseball game: the crack of the bat, the cheering from the bench, the sliding into home plate. But a closer look at the field shows something is very different. They’re playing on a rough grass field, no one is using a batting helmet, fielding glove, or catcher’s mask. From the 1920s through the 1940s, Reed Brothers Dodge had their own company softball team that played on the fields at the Rockville Fairgrounds where Richard Montgomery High School now stands.

Reed Brothers Softball Team playing on a field set up inside the Rockville Fair racetrack oval, circa late 1920s. Photo by Lewis Reed
Fair Now History
From The Daily Mail (Hagerstown, Maryland) 23 Aug 1933:
The historic Rockville Fairgrounds, scene of many harness race programs, will be sold at a sheriff’s sale Friday afternoon at Rockville. The property consists of 26 acres, a dwelling and numerous stables, exhibition buildings and other structures. The sale is being made to satisfy a claim of a bank. It is rumored that the Montgomery County Board of Education will try to buy the grounds as a site for an elementary school and a future location for the entire Rockville educational plant.
Fair Ground Auctioned
From The Evening Sun (Baltimore, Maryland) 26 Aug 1933:
The Montgomery County National Bank submitted the only bid for the historic Rockville Fair Grounds at a public auction on August 25, 1933 to satisfy a bank’s claim. Its bid was $19,500.00 subject to a mortgage held by the Sandy Spring Savings Institution, and unpaid interest and taxes.
The Montgomery County Fair was reborn in 1949 and again started holding its annual Fair in Gaithersburg. On June 4th, 1949, hundreds of volunteers participated in an old-fashioned barn raising and 12 outbuildings were constructed in one day. The site of the new Montgomery County Agricultural Center was created.

June 4, 1949 – Construction of the cattle barns along the railroad tracks. Photo courtesy of Montgomery County Agricultural Fair photo archives.
End of An Era
While many things about the fair have changed over the years, its mission has remained the same.
This event provides the opportunity for 4-H and FFA members to exhibit their livestock, homemaking and craft projects. We also focus on promoting the science and preservation of agriculture in Montgomery County and educating Fair patrons and the community regarding agricultural related topics.
To that end they have been successful since 1846. The Montgomery County Agricultural Fair is now today, one of the largest county Fairs in the State of Maryland.
Find photos like these and much more on Montgomery History’s online exhibit, “Montgomery County 1900-1930: Through the Lens of Lewis Reed“.
References:
Chronicling America: Historic American Newspapers. Library of Congress
Newspapers.com: the largest online newspaper archive
Rockville, Portrait Of A City, Eileen S. McGuckian
Ag Center History
Montgomery Magazine Wheels and Deals Feature
 Reed Brothers is very proud and honored to be featured in the month of August/September 2022 Montgomery Magazine, “Then & Now” section. The black and white photograph above shows the expansion of Reed Brothers Dogde showroom and Gulf Gasoline Station that took place in 1941. At about the same time as the gas station was remodeled, Lewis Reed split up the Sales and Parts and Service operations by constructing a complete new building that was located at the intersection of at Montgomery Avenue and Dodge Street.
Reed Brothers is very proud and honored to be featured in the month of August/September 2022 Montgomery Magazine, “Then & Now” section. The black and white photograph above shows the expansion of Reed Brothers Dogde showroom and Gulf Gasoline Station that took place in 1941. At about the same time as the gas station was remodeled, Lewis Reed split up the Sales and Parts and Service operations by constructing a complete new building that was located at the intersection of at Montgomery Avenue and Dodge Street.
A closer look at the photo reveals the price of gasoline as 15 cents. On the right attached to a telephone pole is a sign pointing the way to Olney. In addition to the Gulf signage there is a small, barely visible sign below that promotes, “Clean Rest Rooms”.
The color photograph above, is the dealership’s location today, now known as Veterans Park. In the 1970s, the site was known as the Francis Scott Key Memorial Park, and later in 1988, it was permanently rededicated as Veterans Park. In the late 1960s, the state of Maryland acquired the land to widen Rt 355 and donated the remaining sliver to the City. The State of Maryland named the connector street behind the dealership’s original location “Dodge Street” following the dealership’s 1941 expansion.
Montgomery Magazine is a lifestyle magazine, with timely articles on county leaders, entertainment, sports, neighborhood and restaurant profiles, entrepreneurs, historic landmarks then and now, plus seasonal special sections of local interest.
Find the issue online at: http://digital.montgomerymag.com/issues/August-2022/index.html
The 100th Anniversary of the Founding of the Montgomery County Police Department

Here posing in front of Reed Brothers Dodge on July 4, 1922 is the first known photograph of the entire MCPD. Pictured left to right: Earl Burdine, Lawrence Clagett, Guy Jones, Chief Charles Cooley, Leroy Rodgers, and Oscar Gaither. Photo taken by Lewis Reed on July 4, 1922.
July 4th marks the 100th anniversary of the beginning of the Montgomery County Police Department. Cattle rustling, bootlegging and stealing poultry were among the most common crimes when Montgomery County hired its first police chief and five officers in July 1922. So widespread was the theft of chickens and turkeys that some residents employed a homespun form of crime prevention by cutting off a specific claw on their birds to identify them. “Officers knew who all the chicken thieves were,” said one historical account of the era put together by the police department, “and upon getting a report of missing Rhode Island Reds, or some other breed, would head straight for the thieves’ hideaway to try to catch them ‘red handed’ before the birds got to the frying pan.”
Posing in front of Reed Brothers Dodge on July 4, 1922 Chief Charles Cooley, center, and his men of the first mounted unit of the Montgomery County Police Force, were on their first day of duty. For several years, since there was no police station, the officers would meet for “roll call” on the steps of the Red Brick Courthouse in Rockville at 2:00 p.m. every day to let each other know they were alive and well. Chief Cooley was given the privilege of a Model T Ford. The chief was paid $1,800 a year (the chief now gets $112,564) while the officers got $1,500. Each of the officers was issued a Harley-Davidson motorcycle, a .38 Smith & Wesson handgun, a black jack, law book and was allotted $300.00 a year for the upkeep of their motorcycle. Jones patrolled Silver Spring, Rodgers the Bethesda-Chevy Chase area and Burdine, Clagett and Gaither the Upper County areas.
The county’s population in the early 1920s was just 35,000 (it’s now more than 800,000). Much of the county was farmland, which accounted for the thefts of livestock. It also was the Prohibition era, when bootlegging and moonshine still factored routinely on an officer’s shift.
The officers worked 14 hours at night, 10 hours in the day, with two days off every two weeks. But they were on call at all times. Since there was no mobile radio contact (the first one-way radio system was installed in cars in the early 1930s), the officers tended to hang around the courthouse or a local firehouse that had a phone.
One of the officers came up with the idea of placing a flashing red beacon light on a pole atop the Rockville courthouse. When flashing, it would alert police that they had a call or were wanted at the office. In 1927, similar lights were used at district stations in Silver Spring and Bethesda.
As part of the 100th anniversary celebration, there will be a Commemorative Ceremony at the Red Brick Court House on July 7, 2022 from 10am-12pm that will mirror the swearing in that took place 100 years ago. The Chief will reveal the contents of the time capsule that was buried 25 years ago, as well as reveal the contents of what will be placed in the new time capsule. This event is free of charge to attend. For more info and other scheduled events, click here: https://www.mcpd100.org/live-events
Congratulations MCPD and thank you for your many years of service!
Dodge “Punishment Pit” – Torture Makes Them SAFER!
Did you know that Dodge Brothers corporation had a “punishment pit”? This pit was a new type of automobile proving ground that was regarded as the quickest and most satisfactory way of finding out how an automobile can stand up under treatment of the most severely abnormal sort. Before Dodge introduced its latest models, some of the test cars were tortured in the punishment pit for as long as 600 hours.
In these trials, every stunt resulting in mechanical agony to all parts was employed to furnish the engineers and builders with proof of the car’s sturdiness and safety, with its ability to “take it.” Where the owner-driver would steer around chuck holes, dams and other obstacles, the punishment pit driver hunts the obstacles, steps on the throttle and tears right into them. He is exceedingly nimble-footed and can let the car turn over without being injured himself.
Not only in the pit is torture applied to the new models. An ingenious device called the “Belgium roll” is almost as cruel to an automobile as the punishment pit. This machine shakes, rattles and vibrates a car placed upon it in such a vigorous manner that many hidden defects are revealed speedily. A few hours of the Belgium roll subject an automobile to more punishment than months of driving over the roughest roads. The effects of vibration on every part are studied closely by the engineer, changes made here and there, and to the public goes the result of torture —
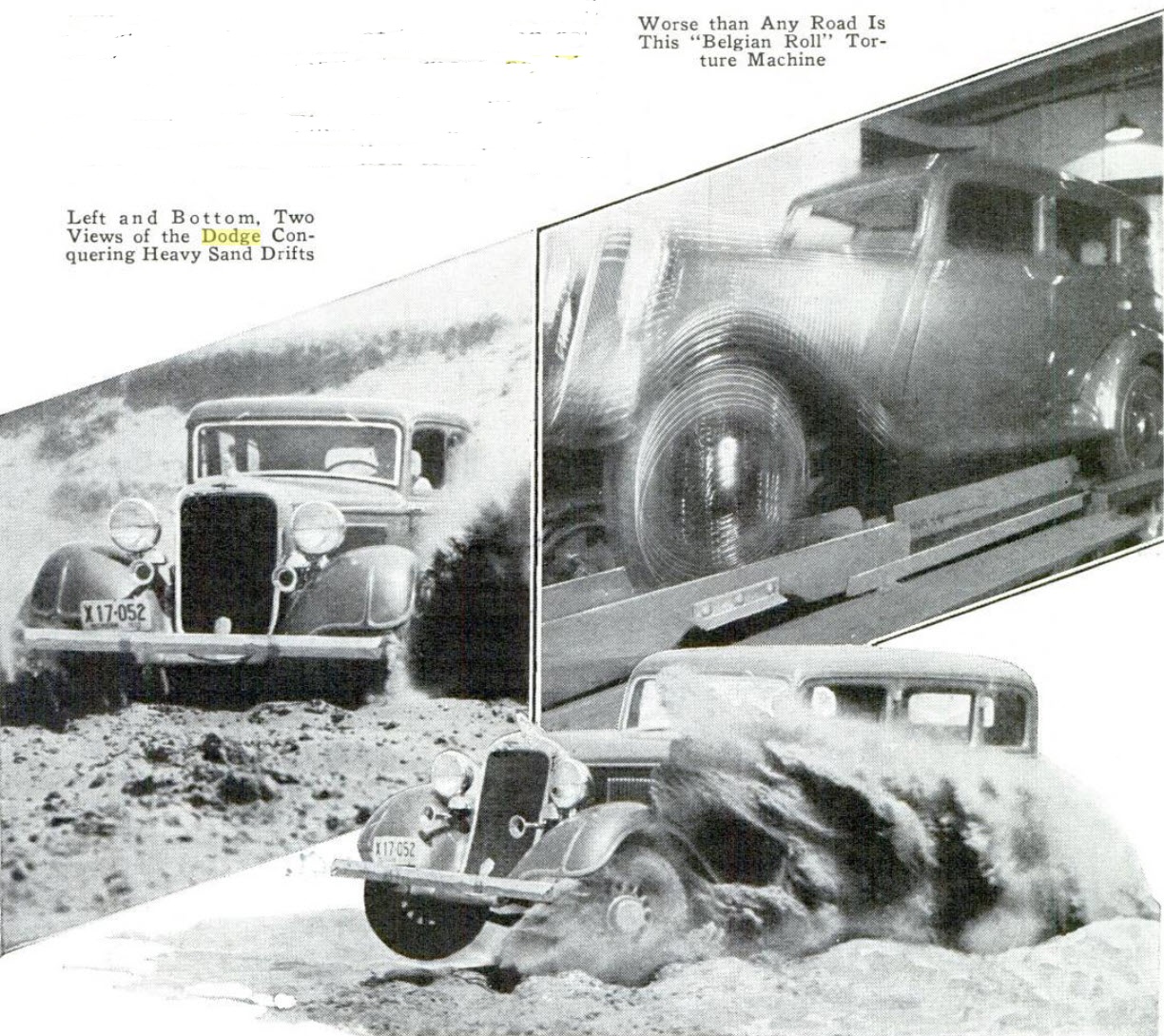 A quiet, safe, smoothly riding automobile that will give years of service.
A quiet, safe, smoothly riding automobile that will give years of service.
One unusual test of motor quietness was conducted by Dodge engineers under military supervision. While the engine was running, an expert rifleman sitting in the front seat fired ten shots with a United States army rifle at a regulation target 100 yards away. During aiming and firing, the rifle rested on the windshield. The result was a 100×100 target score.
Unusual as these tests may appear, they are the means to a common end, that of producing faster, safer and more comfortable automobiles.
Source: Popular Mechanics · Vol. 60, No. 6 · Dec 1933
Some of the Earliest Occupations in Montgomery County
Do you know what a Qwylwryghte, a Stock Maker, or a Hackneyman does? These are some of the old occupations, of which many are archaic, that may show up on old documents relating to our ancestors. Some of the occupations do not exist today or are called other names. Below you can find representations of many varied occupations that Montgomery County residents engaged in during the early 20th Century, though the list is not at all comprehensive.
Blacksmith/Wheelwright/Cabinet Maker
A qwylwryghte — don’t ask me to pronounce it! — is one who makes wheels, or works with wood.
Formerly located on Darnestown Road near the intersection of Seneca Road, Philip Reed operated a blacksmith, wheelwright, and cabinet making business next to his home. These occupations overlapped due to the similar skills they required: the same metal-working tools that were used for horseshoeing could be used to make wheel-rims and other metal wagon parts; the same woodworking skills that created wagons could be used to make pieces of furniture for the home. As late as 1910, there were still approximately 60 blacksmith shops in the county.
Stock Maker
From the June 13, 1940 edition of The Montgomery County Sentinel:
We also read that Philip Reed built up great fame for the town as a maker of gun stocks for sportsmen – he was the father of the Reed Brothers, our local auto dealers. Edgar Reed tells us his grandfather was a cabinet maker and wood carver, but that the wood working talent no longer seems to run in the family.
A Stock Maker carves gun stocks from wood (usually walnut) and fits them to the metal parts of the gun (receiver and barrel). Very high grade firearms may have stocks fashioned from very costly blanks, mostly of one of the walnut varieties, specially chosen for its rare and highly figured grain. The fashioning of high end gun stocks calls for an extremely high level of skill and craftsmanship.
Liveryman
The meaning of Hackneyman is a man who hires out horses and carriages.
Closely related to the blacksmithing and wheelwrighting industry, the livery-stable keeper provided horses that were used in everyday tasks and transportation. The liveryman boarded horses for rent and also provided carriages and wagons. Compared to our modern world, the blacksmith-wheelwright correlates to the auto repair shop, and the livery to the car rental business.
School Teacher
At the turn of the century, teaching was one of the only respectable fields open to educated women who wanted to work. Many unmarried women worked as teachers during the 1900s, and in the early days, they were often required to leave the profession once they were married. The 1920 census indicates that Lewis Reed’s wife, Ethelene (pictured above), was a teacher in the Maryland public school system until her daughter Mary Jane was born in 1922.
Ice Cutter
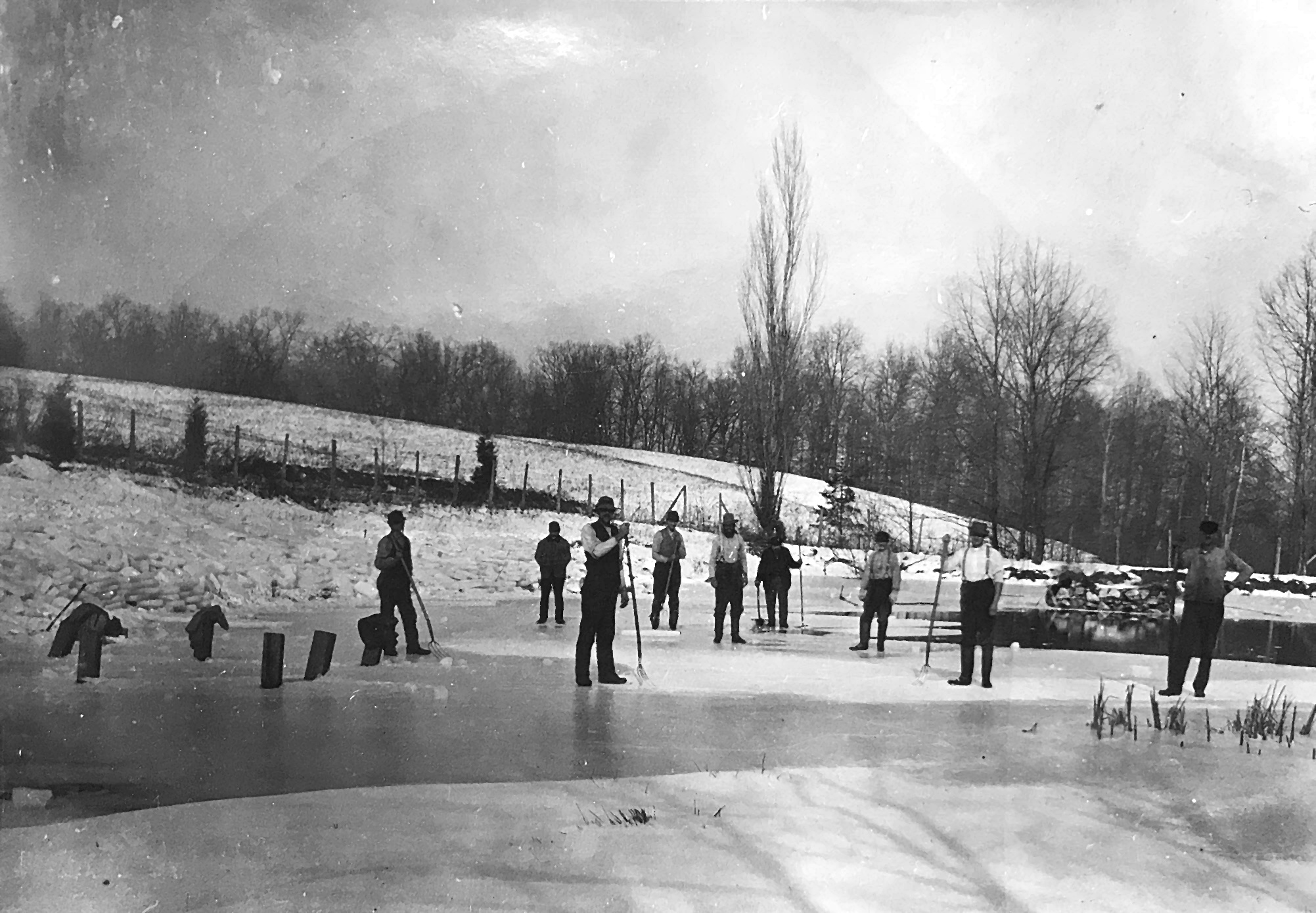

Men harvesting ice with pitchforks and hand saws on a pond in Darnestown, 1910. Note the blocks of ice stacked up along the shoreline.
Most people wouldn’t consider the months of January and February a season of harvest in Darnestown, Maryland. But in our not so distant past, this was harvest time for—ICE. Rivers, lakes and ponds are generally frozen and ice was harvested like a winter crop to keep food cold all summer long. Before modern refrigeration, ice for refrigeration was obtained organically through a process called “ice harvesting.” Ice cutters would risk their lives going out with saws, tongs, and pitchforks to methodically cut and drag blocks of ice from a nearby frozen pond. Those blocks would then be stored in hay-packed ice houses, later distributed throughout towns and cities during the heat of summer. However, people did not put ice in their drinks as we do now. The possibility of debris having been in the water as it froze – even a bug now and then – discouraged the idea.
Store Clerk/Cashier

Clerks at J. F. Collins General Store on East Montgomery Avenue in Rockville, 1914. At left is A. F. “Seen” Beane, who bought this store from Collins in the 1920s and continued doing business in downtown Rockville until his retirement in the 1960s.
The cash register was invented in the late 1800s, and by the 1900s almost every retail organization had one. Store owners sometimes conducted business with their customers, but the more lucrative establishments would hire one or more clerks as assistants to interact with the public. By 1915, more than half of all clerical workers tended to be young women.
Chauffeur-Mechanics
Chauffeur-mechanics of the early 1900s were the first group to earn a living working on automobiles. At the dawn of the early 20th century, society was transitioning from horse-drawn carriages to automobiles. Having grown up in a blacksmith family, Lewis Reed was well positioned to move to the new technology. The 1910 census indicated that 23-year-old Lewis Reed was working as a machinist. Lewis Reed worked as a chauffeur from roughly 1910-1914, before he became involved in the business of selling and repairing automobiles.
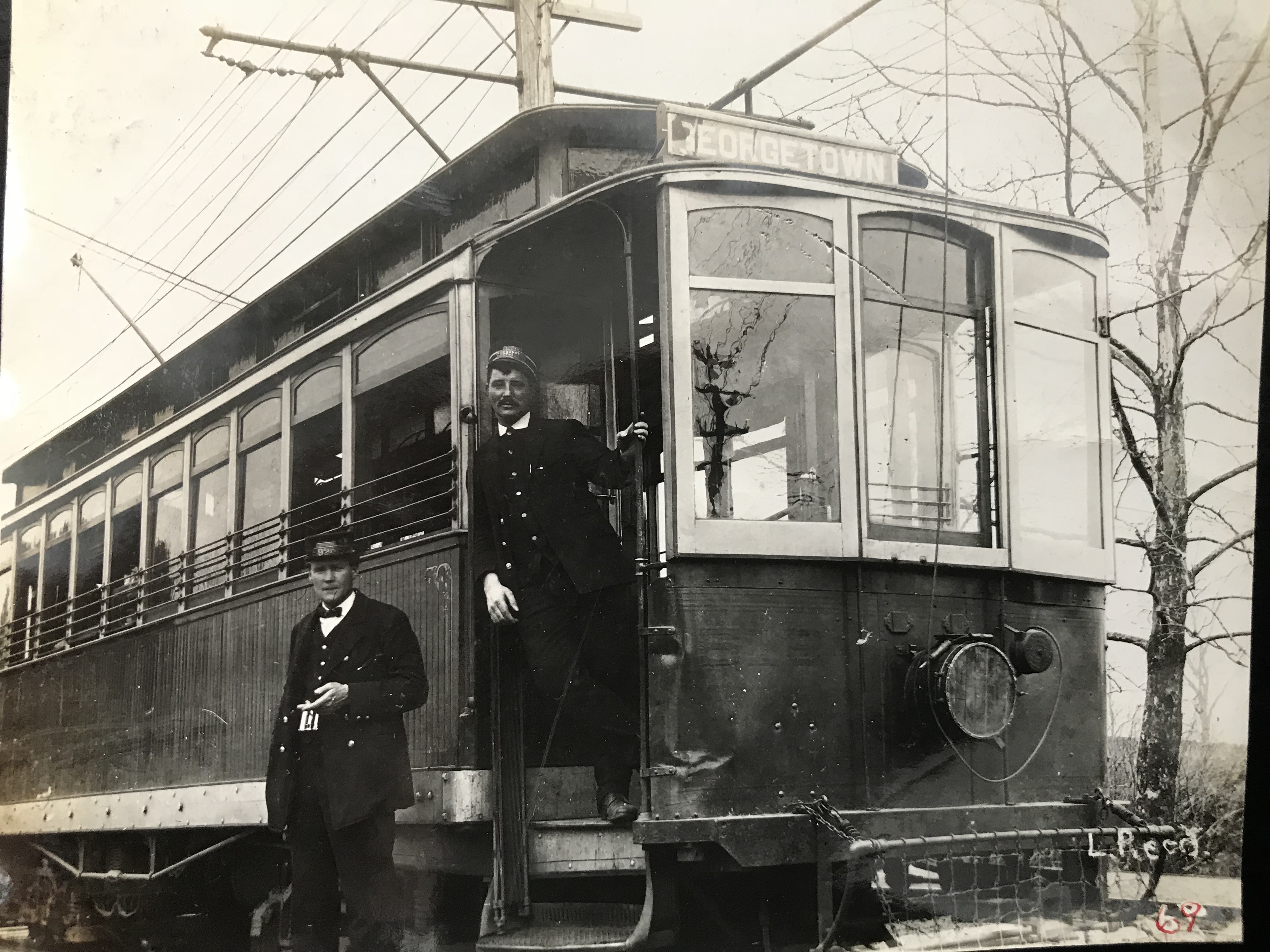
Motorman and Conductors
The debut of Rockville’s trolley cars in 1900 marked the beginning of a golden age of local mass transit. Each car had a two-man crew (a conductor and a motorman) one to operate the car and the other to collect fares.
Mill Worker
A mill is a building equipped with machinery that processes a raw material such as grain, wood, or fiber into a product such as flour, lumber, or fabric. In the 18th and 19th centuries, mills were powered by water in creeks or rivers. In a flour mill, water flowing over the mill wheel was converted by gears into the power to turn one of two burr stones. Kernels of wheat were then ground between the two stones. The grinding removed bran (the outer husk) from the wheat kernel, and then crushed the inner kernel into flour.* Flour mills were an important part of rural communities across the country, including Montgomery County, and millers were respected members of their community.
Farmer
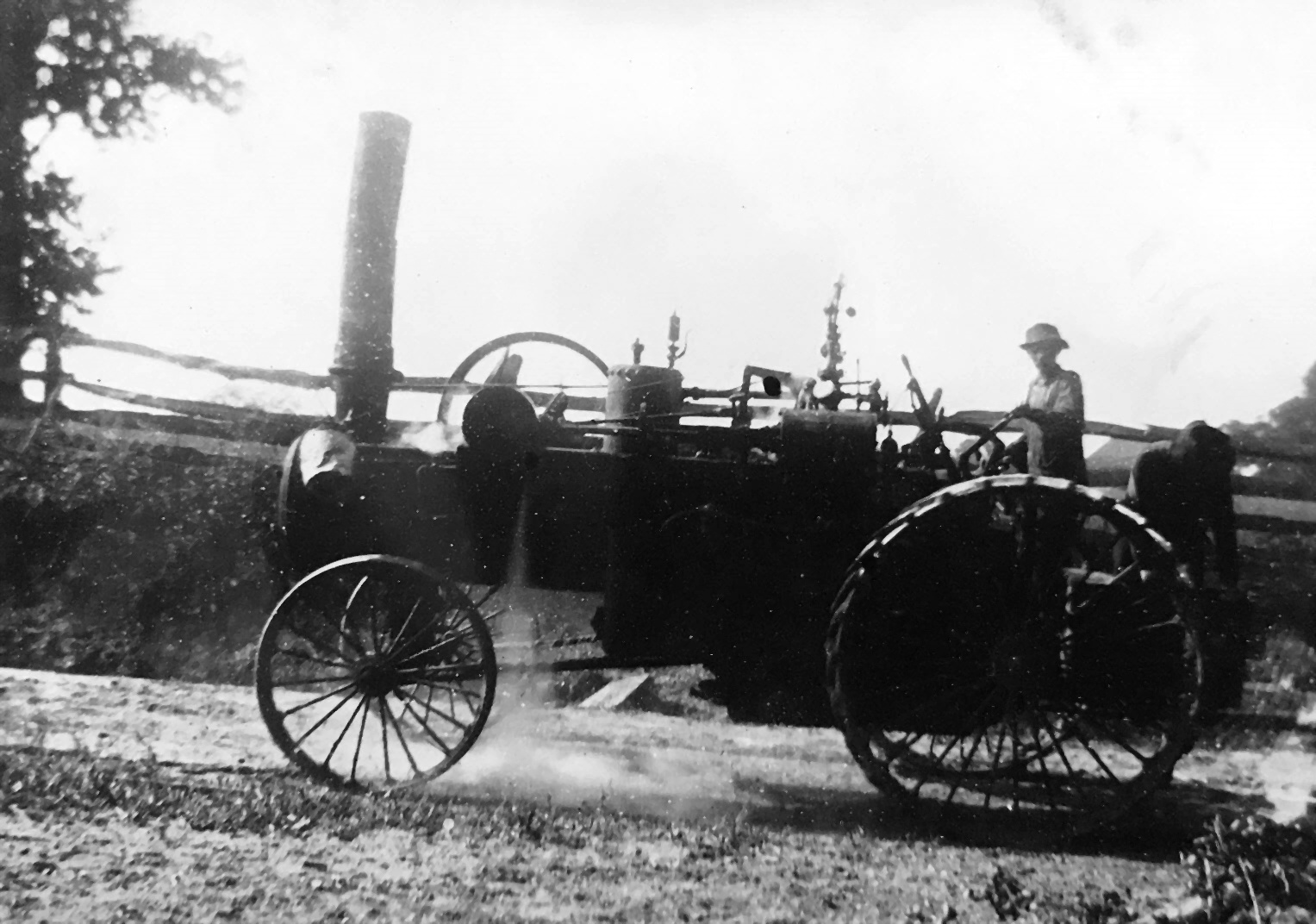

An agricultural tractor powered by a steam engine, a design used extensively in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
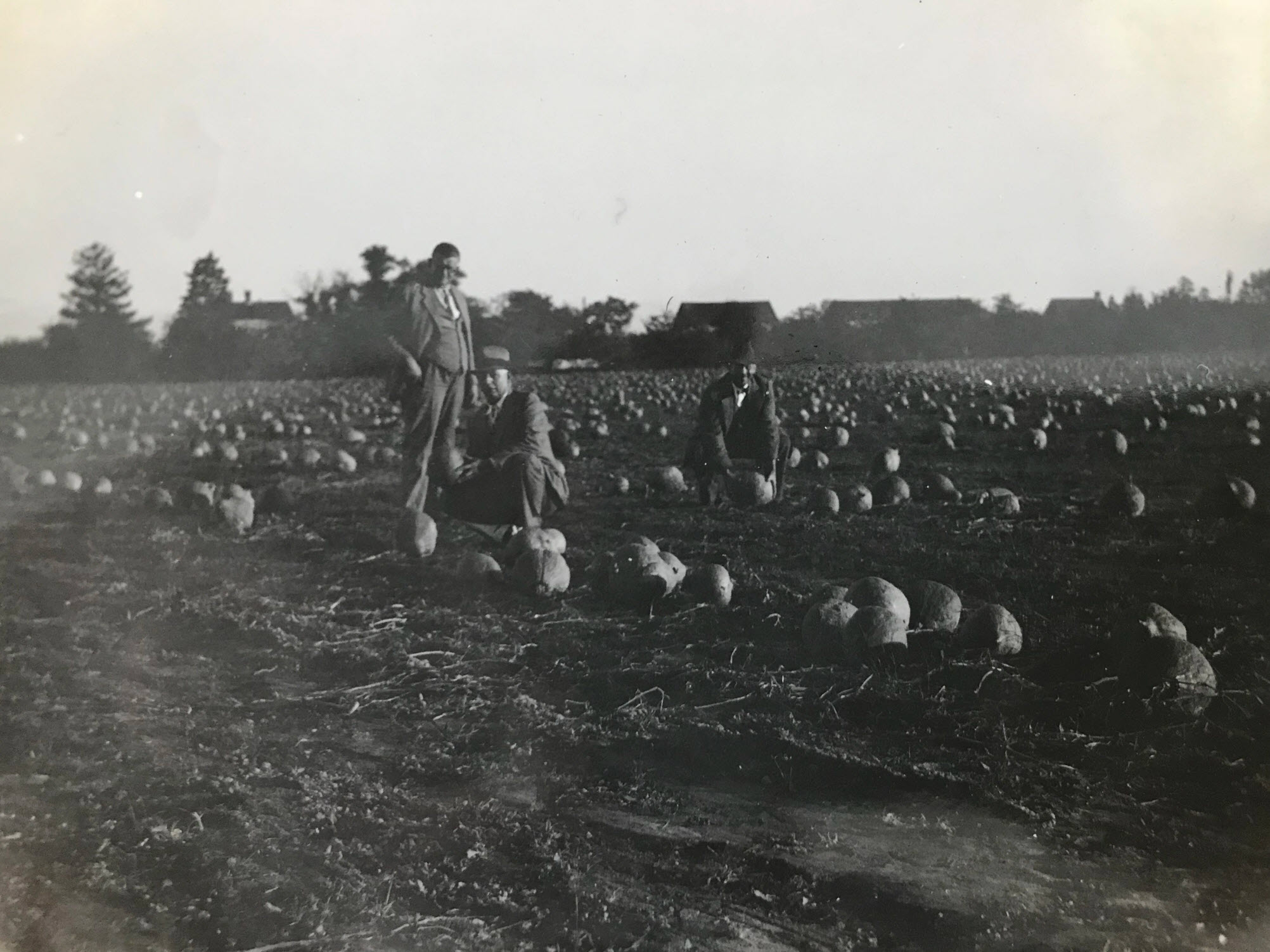
Above is a photograph of three men in suits pumpkin picking in Thomas Kelley’s field of pumpkins in Pleasant Hills, circa 1920. Tom Kelly farmed much of the land around the Pleasant Hills homestead and was famous for his “Kelly Corn” farm wagon of fresh dairy produce during the summer months, as well as the corn that fed visitors to the Montgomery County Fair each August and, of course, his pumpkin patch in the fall.The turn of the century was a time of transition, and the families who went from horses to tractor horsepower witnessed the birth of mechanization on the farm. The newest farm machinery to hit the market near the turn of the 20th century were traction engines powered by steam; essentially the predecessor to today’s modern farm tractor. They could plow, they could haul, and you could put a big belt on the fly wheel and drive a saw mill. The engines would normally run on coal, wood, or even straw: whatever would sustain a fire.
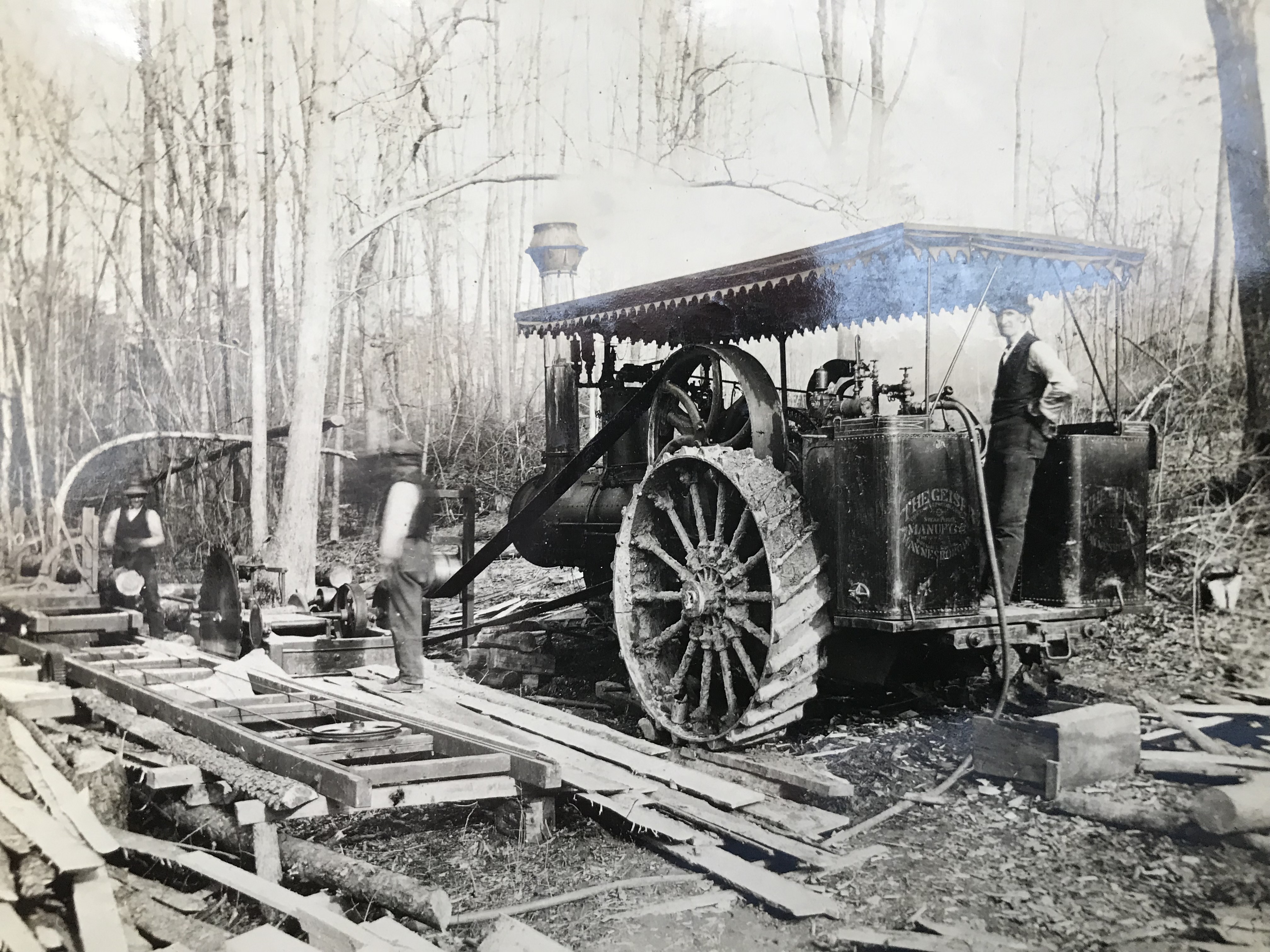

Francis Flack of Montrose on steam tractor with roof, 1909. Built by Geiser Manufacturing Company, makers of the Peerless line of steam tractors.
Steam helped improve the efficiency of most farm chores, including plowing, planting and harvesting. And steam-powered equipment also was used for other heavy duty tasks, including rock crushing and wood cutting, to aid in clearing the land. Francis A. Flack (1875-1961), a life-long resident of Montgomery County, was a successful farmer in the lower section of the county near Garrett Park. The work depicted below–sawing felled trees into usable lumber–took place on his farm in 1909. Flack is pictured in the lower left photo.
I remember that engine as though I had seen it only yesterday, for it was the first vehicle other than horse drawn that I had ever seen. It was intended to drive threshing machines and power sawmills and was simply a portable engine and a boiler mounted on wheels.
It was the steam traction engine that inspired Ford to design and manufacture automobiles. By the early 1930s, gasoline-powered farm equipment, evolved from the automobile industry, had mostly replaced steam powered machines.
Road Worker (Heavy Equipment Operator)
Building a road requires moving earth and rocks, leveling the roadbed and digging trenches for drainage ditches. These tasks fell to those who operated the large steam-powered excavating machines and steam shovels. Pictured above are rare, historical photographs that Lewis Reed took of the construction of Massachusetts Avenue in Washington, DC as it was being graded in 1912. (click on thumbnails to view gallery)
A steam shovel is a large steam-powered excavating machine designed for lifting and moving large amounts of heavy material such as rock and soil. Steam shovels played a major role in public works in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. When digging at a rock face, the operator simultaneously raises and extends the dipper stick to fill the bucket with material. When the bucket is full, the shovel is rotated to load the railway car. Steam shovels usually had a three-man crew: engineer, fireman and ground man.
Census Taker
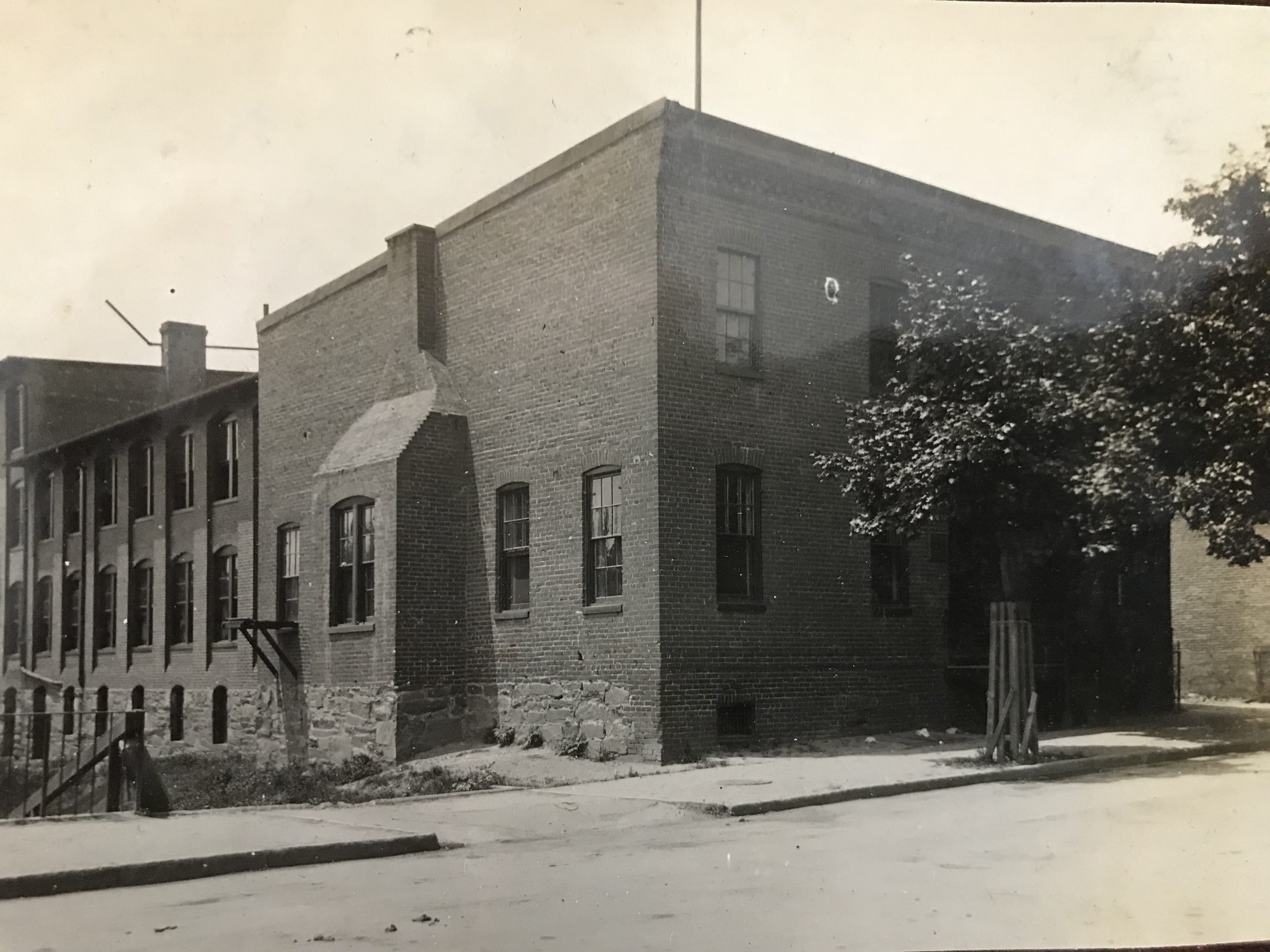

Two-story building that housed Hollerith’s card manufacturing plant, assembly plant, repair shop, and development laboratory, as it appeared in 1911.






































Recent Comments