Reed Photo Collection Highlight: Early 20th Century Motorcars
Each of the images below from Lewis Reed’s Collection has a car included, whether as a center point of a family photo, in the background of life’s moments, or on a cross-country road trip. These photos give a snapshot not just of the cars at the time, but a peak into an important aspect of the everyday lives of County residents.
There were no paved highways for automobiles to shoot along at 60 and 70 miles an hour; just country roads, filled with ruts, sand, and mud, over which no one wanted to drive at the maximum speed of passenger cars, which was about 30 miles an hour. But every trip was a different adventure.

In the early 20th century, traveling cross-country by automobile was intimidating, if not a little bit dangerous. Cars were unreliable and roads were rough. The child in the photo is my mother, Mary Jane Reed Gartner. Photo by Lewis Reed
A cross-country road trip is a quintessentially American experience. It’s always an adventure, but in modern times it’s a relatively tame one: The roads are paved, signs point the way, and Siri always has your back. If cars had cup holders back then, these folks would be rolling with crystal goblets, not Big Gulps.
Come away with me, Lucille: In my merry Oldsmobile: Down the road of life we’ll fly: Automo-bubbling, you and I….

Ethelene Thomas Reed, who married Lewis Reed in 1921, is sitting in passenger seat of a circa 1918 Oldsmobile Club Roadster and her sister, Celeste Thomas Brown, is sitting behind her in the back seat. Photo by Lewis Reed

1918 Oldsmobile Roadster shown with Ethelene and her sister Celeste behind the wheel. Photo taken by Lewis Reed at the Clinton Clay Thomas family farm which was located on Butterfly Lane in Braddock, Maryland. Photo by Lewis Reed
Back in the early part of the last century when the automobile was still new and a novelty, it was often used for Kodak moments.

Two ladies posing in a 1911 Speedwell Touring car. Check out the humongous steering wheel! Photo by Lewis Reed
The photographs below was taken by Lewis Reed on one of his many cross country road trips. The car is a 1935 Dodge Touring Sedan with Maryland Dealer license plates. Note the rear-hinged “Suicide Door”. Cars of this era did not have seat belts, so there was nothing to hold a passenger in the car. The term “suicide doors” was therefore placed on vehicles with the rear-hinged door configuration, the theory being that the forward motion of the car could cause the door to fly open, possibly causing the unlucky person sitting next to the door to be pulled out of the car, or the door itself could be ripped from its hinges.

I have no idea what prompted my grandfather to take a photo at this location, but perhaps it was the amazing view in the background. Photo by Lewis Reed
In order for occupants of early 1920’s cars to remain warm during the cold winter months, especially when it was snowing, it was necessary for them to dress warmly and cover themselves with blankets. Note the car in the photo below is mostly open-bodied, with no windows and certainly no heat. Tire chains are on the rear tires. I cannot say with any certainty, but I believe it is Lewis Reed’s car with his wife and baby daughter, Mary Jane, sitting inside all bundled up.
Early motorists weren’t afraid to drive in the snow simply because they didn’t have 4-wheel drive and electronic assistance; they just got out and did it. Who would dare go out in these conditions today without an AWD SUV and heated seats?

Car stopped (stuck?) on snowbound road. Although no tire chains are in evidence, they might have been useful coming up that hill. Photo by Lewis Reed
Nobody really thinks about it today. If your car is too cold, then simply switch on the “heater” and soon your car will be warm. However, it wasn’t always that way. What passengers did back then, in the early days of motoring, was bundle up as if one was outdoors. This meant heavy clothing, winter gloves and snow boots. It wasn’t long, however, before car makers realized that a few comforts, like heat in the passenger compartment, or even some type of heated seating, would help sell cars.

Lewis Reed’s 1920 Oldsmobile stopped along Goshen Road outside rural Gaithersburg. Photo by Lewis Reed
In 1900 car owners were almost by definition wealthy, especially since they often employed chauffeurs: many wouldn’t have dreamed of trying to operate their own vehicles. The earliest car owners had no real repair business to turn to. To be a successful motorist in the early 1900s, you needed to have some sort of mechanical skills. Or you had to find someone who did. Wealthy people employed private chauffeur-mechanics to not only drive, but also maintain and repair their large, expensive automobiles — rather than learn to do it themselves. Chauffeurs would be in charge of everything to do with the owner’s motor vehicle including repairs and maintenance and cleaning this meant that early personal chauffeurs had to be skilled mechanics. Pierce-Arrow was one of the most common makers of luxury cars in the early 20th century. The price for one of these vehicles was sometimes as much as ten times the price of a standard touring car.

Two ladies with parasols are sitting in the landaulet section of an early Pierce-Arrow limousine, while chauffeur Lewis Reed tends to the motor. The rear portion of the limousine is partitioned from the driver with a glass shield, and covered by a convertible top, which you can see is currently in the lowered position behind the ladies. Ca. 1910

Chauffeur Lewis Reed (left) in the 1914 photo above poses with an unidentified family and their Pierce-Arrow Model 48.
Early automobiles were unreliable. They broke down frequently and needed to be pulled out of mud or snow by horses. They meant it back in the good old days when motorists were advised to “get a horse”. The photo shows William Beall in his 1915 Pullman in front of old St Mary’s Church and his younger brother Vernon on horseback “towing” him to Reed Brothers.
The touring car was one of the most common styles of automobile in the early decades of the 20th century. Nearly every auto manufacturer offered a vehicle in this style. Touring cars generally were denoted by an open body seating four or more people. Identified by the triangle logo on the grill and the number of passengers seated in it, the car below appears to be a 1918 Hudson Super Six Seven Passenger Touring. The Hudson and Oldsmobile were sold at Reed Brothers from roughly 1917 through 1923.
Vehicles required much higher road clearances than modern cars due to the poor state of roads and tracks, hence the large diameter skinny tires of the day which were effective at cutting through mud to reach more solid ground.

Early touring car with its top down. The folded top behind passengers was known as the “fan” when in the down position. Photo by Lewis Reed
The popularity of the touring car began to wane in the 1920s when cars with enclosed passenger compartments (i.e. fixed steel roofs) became more affordable, and began to consistently out-sell the open cars.
The touring car body style was popular in the early 20th century, being a larger alternative to the two-seat roadster. The photo below was taken in 1915 by Lewis Reed in front of the original Rockville Garage. Old St Mary’s Church is in the background. Note the unpaved dirt road on Veirs Mill Road. Rockville Garage was a distributor of Fisk Tires until circa 1918, when they replaced it with the Firestone brand. The car appears to be a 1916 Studebaker Roadster. The roadster was a sportier style of vehicle, usually a two-seater with a convertible canopy roof. Many manufacturers offered roadster versions of their larger touring car models.

This photo was taken by Lewis Reed across from Reed Brothers Dodge, circa 1915. Old St Mary’s Church is in the background. Photo by Lewis Reed.
Ever want to see how sausage is made? Well, okay – maybe not… but this interesting photo taken by Lewis Reed some 100 plus years ago allows you to see how 18 men managed to cram themselves into a 1910-1911 Pierce Arrow Model 48 7-Passenger Touring. Pierce-Arrow Motor Car Company in Buffalo, New York, produced some of the finest automobiles made and was one of the most popular high-quality cars of the time.
The automobile has affected this country more than any other invention of its time. Without automobiles, life as we know it would not be the same, and the changes that they have brought can be seen in every aspect of our lives.
Lewis Reed Captures the Thrill of Motorcycle Racing in 1915

A motorcycle racer rips down an unknown racetrack kicking up dust in his wake. Photo by Lewis Reed, ca. 1915
In the first years of the twentieth century, companies like Harley-Davidson and Indian began producing motorcycles for the general public. Although there is not an exact date of the first motorcycle race, you can be sure that as soon as there were two motorcycles on the road, there was racing. As more and more motorcycle manufactures started popping up across the U.S., motorcycle racing started making it’s way to more official venues. The earliest races were held on fairground dirt tracks used for horse racing.
This photograph taken by Lewis Reed shows an unknown racer at a fairground raceway in the early 1900s. In the teens, motorcycle racing on dirt tracks throughout the country, was one of the most popular spectator sports. Despite the danger to both racers and spectators, the motorcycle races became very popular and drew large crowds of spectators. Motorcycle racing continued until just after World War 1, when the focus shifted to automobile racing.
How Old Cars Were Heated
Nobody really thinks about it today. If your car is too cold, then simply switch on the “heater” and soon your car will be warm. However, it wasn’t always that way. What passengers did back then, in the early days of motoring, was bundle up as if one was outdoors. This meant heavy clothing, winter gloves and snow boots. It wasn’t long, however, before car makers realized that a few comforts, like heat in the passenger compartment, or even some type of heated seating, would help sell cars.
In order for occupants of early 1920’s cars to remain warm during the cold winter months, especially when it was snowing, it was necessary for them to dress warmly and cover themselves with blankets. Note the car in the photo below is mostly open-bodied, with no windows and certainly no heat. Tire chains are on the rear tires. I cannot say with any certainty, but I believe it is Lewis Reed’s car with his wife and baby daughter, Mary Jane, sitting inside all bundled up.
While this had been the accepted way to do things for centuries, it did not take long for automotive engineers to realize that heat from the car engine could also be used to warm the interior of the vehicle. Heaters became standard equipment on the more expensive cars and over time they were fitted to most cars. You could buy and fit after market car heaters to suit cheaper cars like the Fords and Chevrolets.
Below are some advertisements from an Automotive magazine of 1922 that show the two different ways motorists used to keep warm – the rug and the heater.
LAIDLAW MOTOR ROBES
An essential appointment in your own car. A seasonable gift for a friend.
BEAUTIFUL AND COMFORTABLE
You have your car insured against every possible contingency of accident, fire, theft, etc.,—but how about its occupants– can you guarantee their comfort against winter’s storm and cold?
LAIDLAW MOTOR ROBES are COLD INSURANCE, you pay no premiums on their price, yet you receive protection of warmth, comfort and luxury.
LAIDLAW MOTOR ROBES are made in an infinite variety of color and fabric, lined or not, as you wish. Monogrammed at but slight additional cost. Prices exceptionally low. Quality exceptionally high. Order now for holiday gifts.
Comfortable Driving at Zero!
THE KINGSTON CAR HEATER stands between you and the coldest wind that blows. It is a heater that keeps your car warm at zero weather, that warms the car with pure, fresh air, that can be instantly adjusted to meet your wants, that is beautifully and substantially built — an ornament to any car.
Note the new low price
DEALERS everywhere should order their stock of Kingston Heaters at once. Last year when cold weather came the demand was so great that some orders were delayed. This year, with greatly increased production, with a finer heater, and with the new low price the sales of Kingston Heaters will break all records.
FORD Model Complete $3.75
Chevrolet, Overland, Dodge $5.00
How “Suicide Doors” Got Their Name
So why are these doors called suicide doors? Did someone commit suicide with one? What’s suicidal about a door?
The theory is that the forward motion of the car could cause the door to fly open, possibly causing the unlucky person sitting next to the door to be pulled out of the car, or the door itself could be ripped from its hinges. It’s debatable as to whether this was speculation or reality, but cars of this era did not have seat belts, so there was nothing to hold a passenger in the car.
Think about it. Imagine trying to open a conventional front door while you’re driving 70 mph. It’s going to be increasingly difficult because of a simple fact of physics: air pressure. The farther you open the door as you’re sailing down the highway, the more air is going to hit the door, forcing it back. Hopefully, the end result is that it never opens far enough for you to fall out.
Now, imagine accidentally unlatching a door that opens the other way. Instead of working to keep the door shut, the road wind serves as an accelerator, helping to fling the door open and maybe you with it as you grab for the handle in a panic to close it. To add insult to injury, you’ll likely be whopped by the door as you fall out. The term “suicide doors” was therefore placed on vehicles with the rear-hinged door configuration, the theory being that anyone inside was on a suicide mission because of the design.
Another urban legend about the origins of the suicide doors maintains that 1930s gangsters liked the door design because it made pushing someone out of a moving car easier. If that were true, though, wouldn’t the correct term be “homicide doors”?
Suicide doors were favored in pre-war automobiles throughout the the 1930s. They were fairly common on many domestic and imported car makes in the 1930s. A forward-opening door — either in front or back — permitted easier access and egress — especially for women in long skirts or dresses. Hinging the front door at the rear also facilitated a more slanted windshield.
As a result, manufacturers understandably have tried hard to bury the old “suicide doors” reference. Today, you’ll find such killer names as “RAD” or “rear-access door” (Saturn), “freestyle doors” (Mazda RX-8), “coach doors” (Rolls Royce), “FlexDoors” (Opel), “scissor doors” (Lambo), “clamshell” (Toyota), and “rear-hinged doors” (preferred technical term).
Now, About That Name…
So where did the name “suicide doors” come from, then? You’ll find multiple explanations, none definitive. The fact that no historian can verify the origins of this bit of slang only adds to the mystique.
Source: Wikipedia





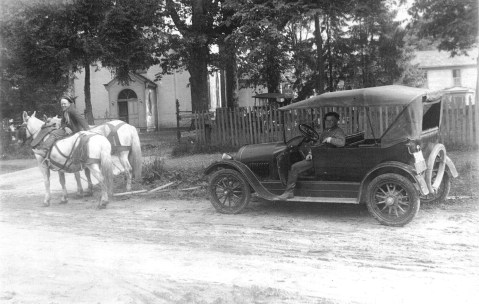




















Recent Comments